Introduction
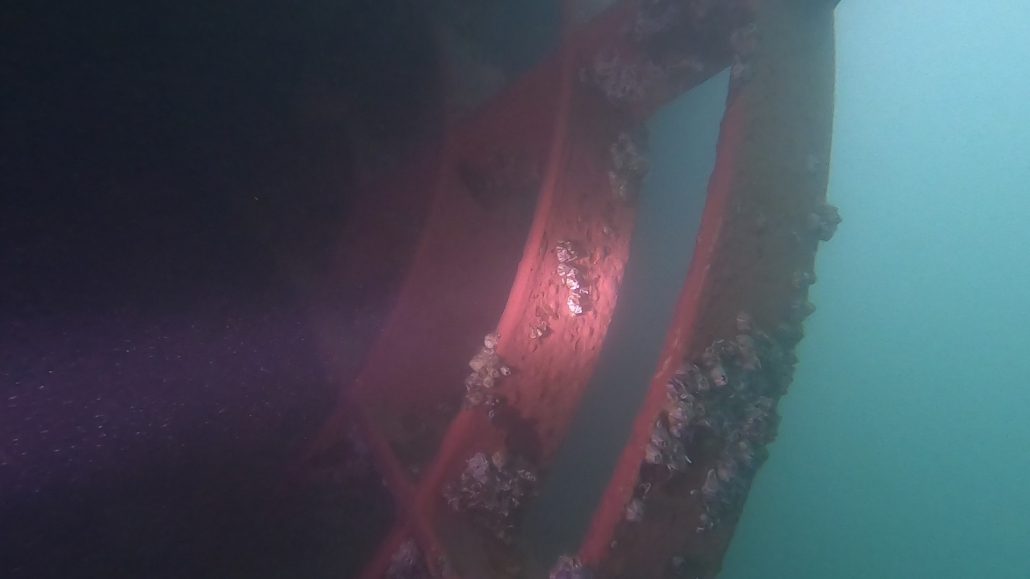
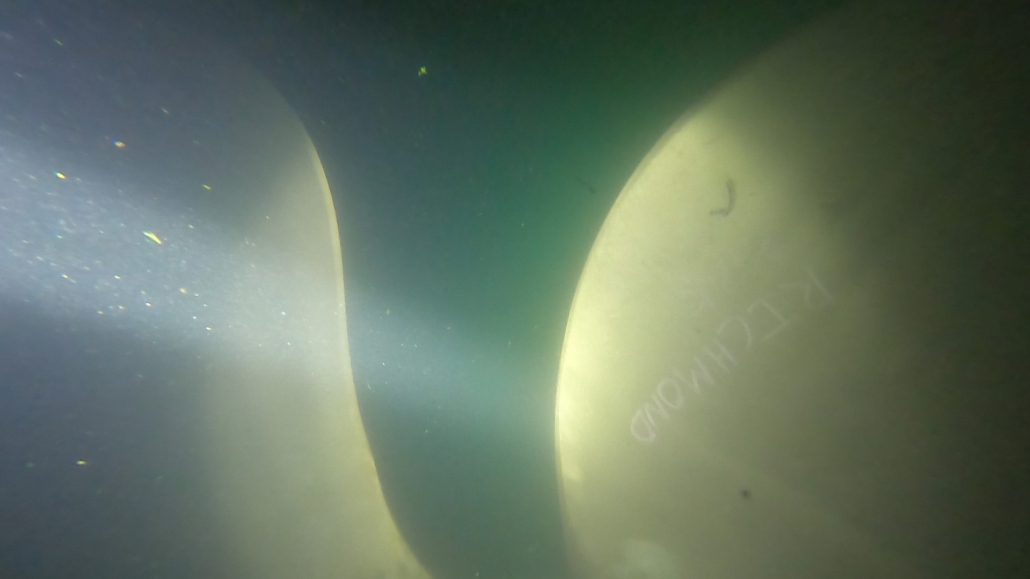
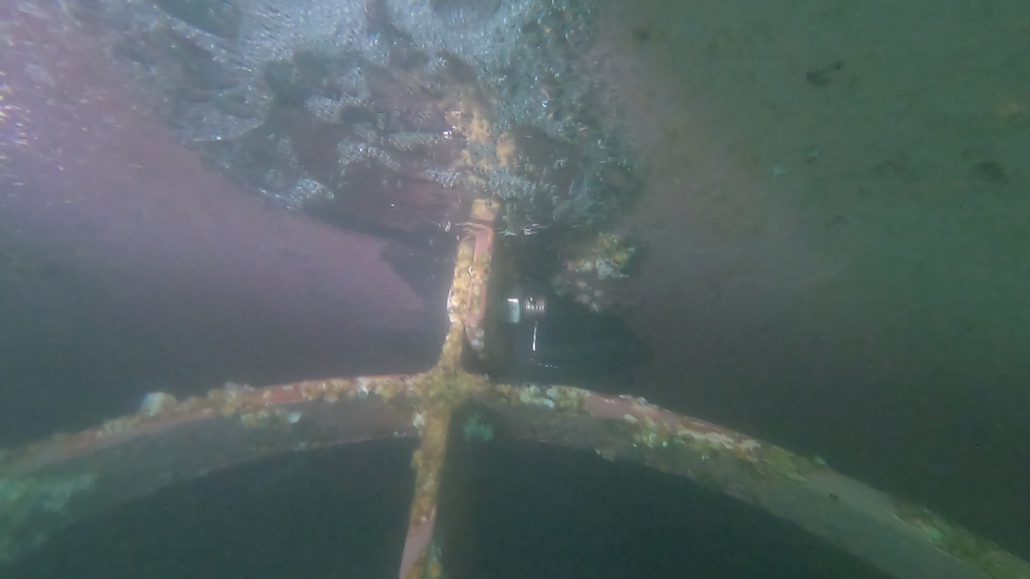
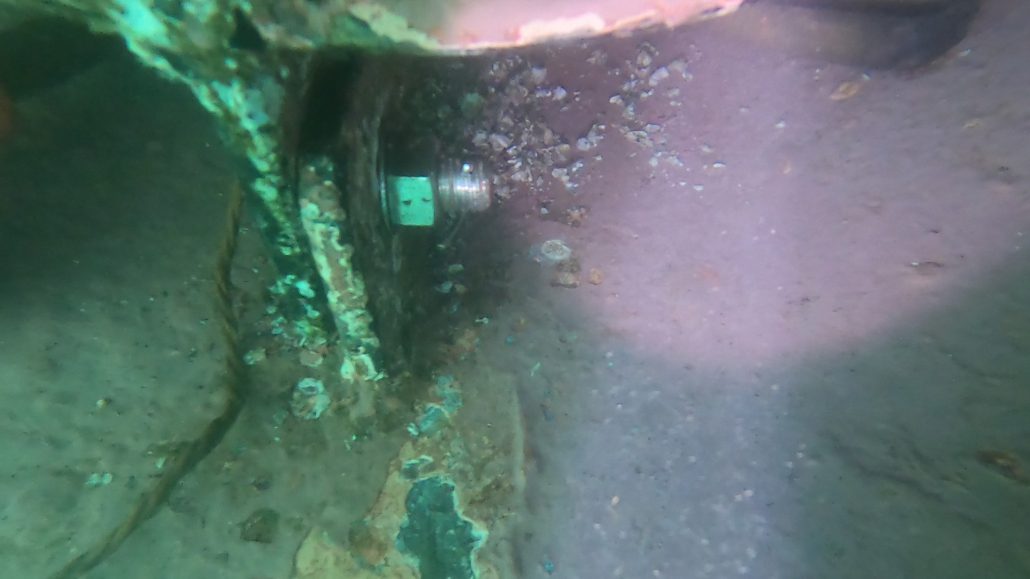
Oil leakage at a ship’s propeller is a critical issue that can lead to mechanical malfunctions, high maintenance costs, and significant environmental impacts. Early detection of leaks is essential to prevent further damage and ensure continuous maritime operations. Underwater inspection is an effective method for identifying the source of the leak and precisely locating the affected area, particularly on the propeller blades, the hub (or boss) of the propeller, the Simplex system, and the section between the Simplex and the propeller.
Possible Causes of Oil Leakage
Oil leaks can result from several factors, including:
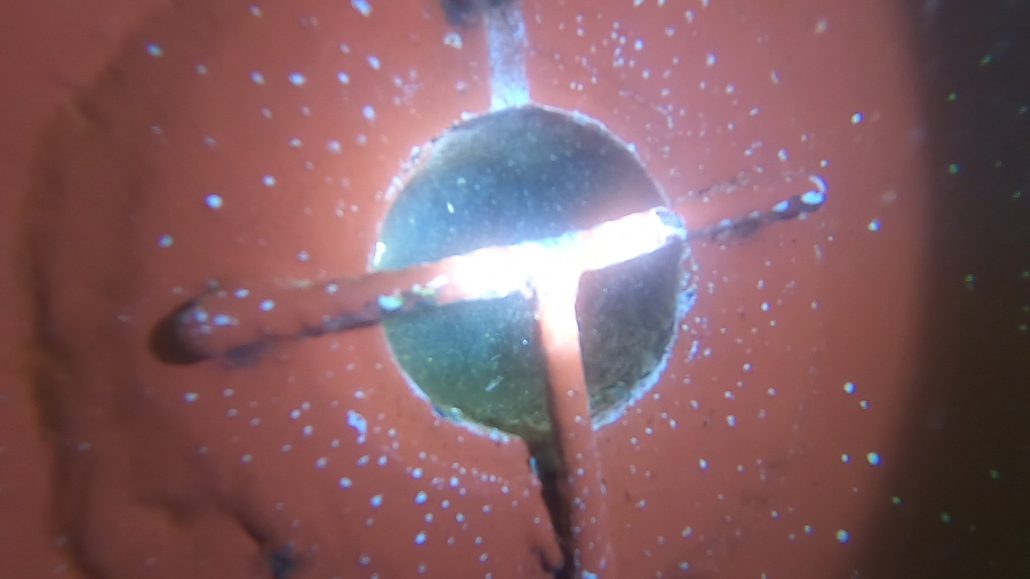
- Wear of Simplex system seals: The Simplex system, which ensures the seal between the propeller shaft and the stern tube, may naturally wear over time, leading to oil loss.
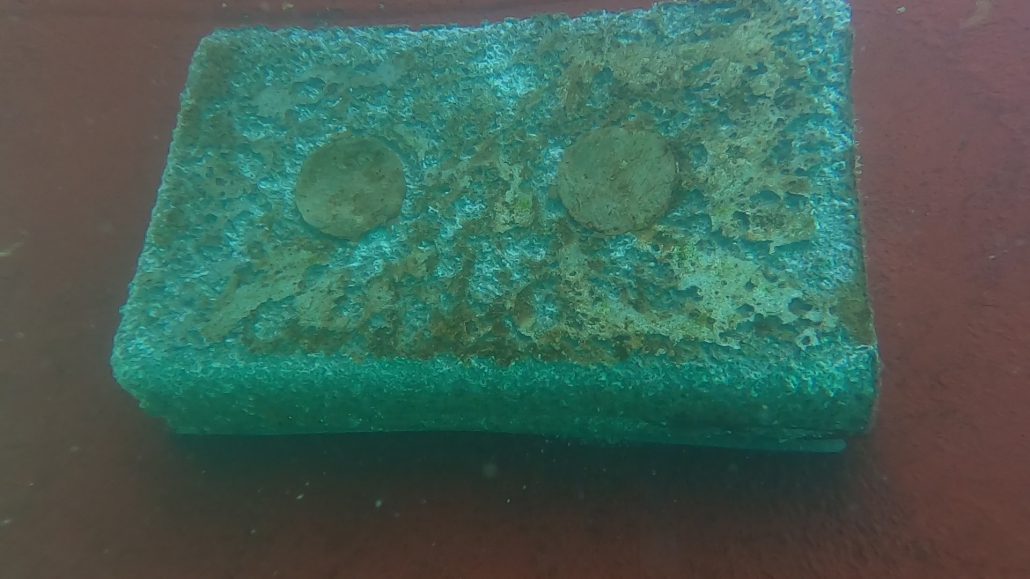
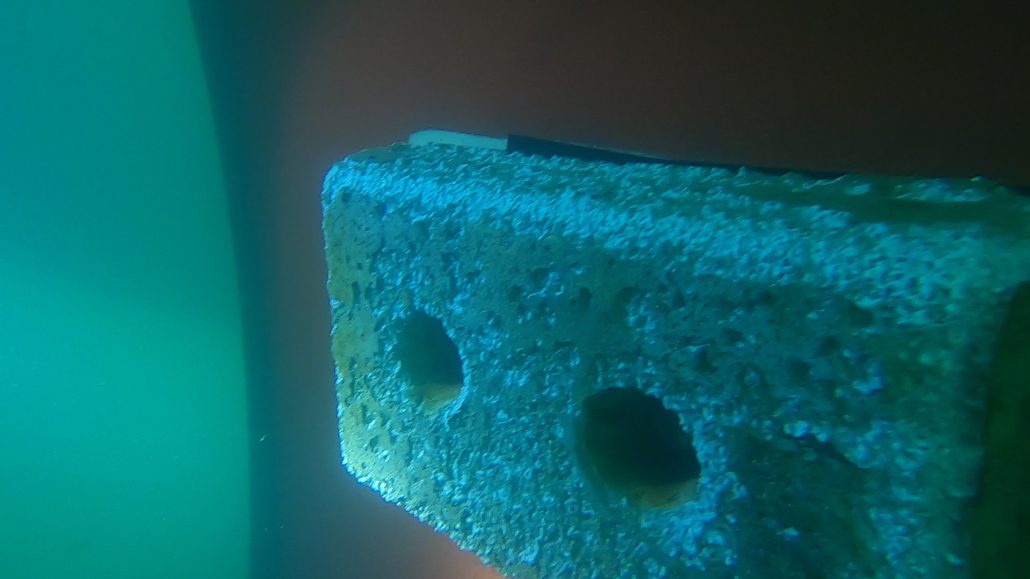
- Microcracks on the propeller hub: Repeated mechanical stress, cavitation, or impacts can cause cracks on the hub, resulting in an oil leak.
- Seal failure between the Simplex and the propeller: Poor installation or seal wear can compromise the system’s tightness, leading to a gradual leak.
- Deformation or damage to propeller blades: Impact with a floating object, fishing net, or quay contact can cause cracks or displacement of propeller components, affecting oil system tightness.
Importance of Underwater Inspection
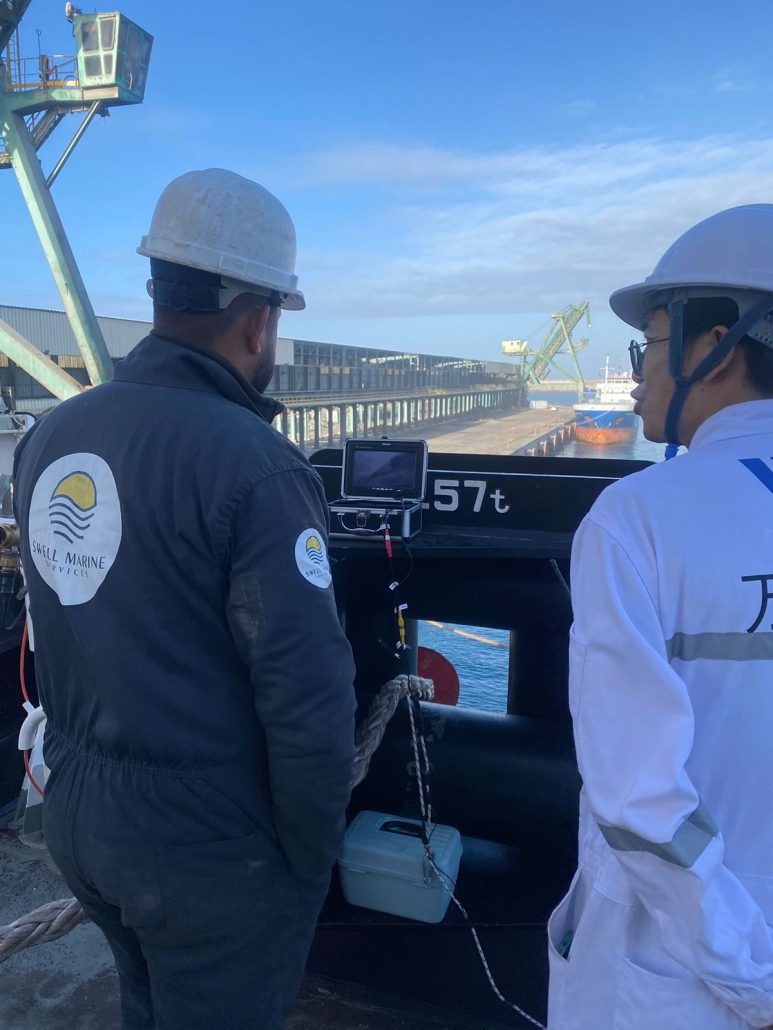
Underwater inspection is a fast and effective way to identify the cause of oil leakage without dry-docking the vessel. It offers several advantages:
- Precise Leak Location: Using specialized divers or underwater drones (ROVs), it is possible to visually inspect the propeller and its components to detect the origin of the leak.
- Prevention of Further Damage: An undetected leak can worsen and lead to costly long-term damage, particularly to the propeller shaft and stern tube.
- Reduced Vessel Downtime Costs: Underwater inspection provides an initial diagnosis without requiring immediate dry-docking, optimizing maritime operations.
- Compliance with Environmental Regulations: Oil leaks in water can have significant ecological impacts. Rapid intervention helps limit pollution and avoid regulatory penalties.
Underwater Inspection Methodology
The inspection follows several steps:
- Preparation and Briefing: Defining the inspection area and selecting appropriate equipment (high-definition cameras, ROVs, underwater lighting, etc.).
- Examination of Propeller Blades: Checking for cracks, impacts, or deformations.
- Inspection of the Propeller Hub: Analyzing seal conditions and searching for visible leaks.
- Checking the Simplex System: Verifying the condition of seals and connections between the Simplex and the propeller.
- Reporting and Recommendations: A detailed report is provided with observations and recommended solutions (underwater repair, dry-docking planning, seal replacement, etc.).
Trust Swell Marine Services for Reliable and Efficient Underwater Inspection!
With years of experience in underwater inspection and maintenance, Swell Marine Services offers a team of qualified experts to detect and resolve any oil leaks on your propeller. Our certified divers and state-of-the-art equipment ensure rapid, precise intervention that meets international standards. Don’t let an oil leak compromise your vessel’s performance and safety—contact us today for a professional inspection!
Conclusion
Oil leakage at a ship’s propeller is a serious problem requiring prompt intervention to avoid costly and environmentally damaging consequences. Underwater inspection is an effective solution for locating leaks, determining their cause, and implementing necessary corrective actions. By integrating this method into preventive maintenance, shipowners and operators can enhance fleet reliability while reducing operational and environmental risks.